Quick Start
Dive into the most straightforward and recommended way to use IRIS with Docker, detailed below.
Pre-requisites
Hardware 💻
IRIS is designed to be lightweight yet scalable, running smoothly on small laptops or powering large organizations. For a typical instance of 10 users, daily usage of ~200 alerts, and a few ongoing cases:
- CPU : 8 cores
- RAM : 32 GB
- Storage : 1 TB fast SSD
Keep in mind that the database can grow rapidly, and modules may require more resources depending on their specific purposes.
Docker 🐳
IRIS requires Docker and Docker Compose for building and running the project. For installation instructions visit the official Docker website.
The platform is officially supported on most Linux and MacOS systems. While it should work on Windows, some changes may be necessary to the dockerfiles for file storage paths.
Versioning 📈
Production-ready code is always tagged with a specific version number. Alpha and beta versions are not production-ready, so please avoid using the master branch for live environments.
Run IRIS 🏗️
To run IRIS, follow these steps:
-
Clone the
iris-webrepository: -
Check out the latest non-beta tagged version:
-
Copy the environment file
Warning
The default configuration is suitable for testing only. To configure IRIS for production, see the configuration section.
-
Pull the Docker containers:
-
Start IRIS:
IRIS should now be accessible on your host interface via HTTPS protocol, port 443 by default. You can access it through your web browser using https://hostip.
Upon first start, an administrator account will be created. The password is printed in the console output and can be found by searching for WARNING :: post_init :: create_safe_admin in the logs. Alternatively, you can define an admin password at the first start using the IRIS_ADM_PASSWORD environment variable in the .env. Please note that this setting has no effect once the administrator account is created.
Info
If you don't find the password in the logs, try running docker compose logs app | grep "WARNING :: post_init :: create_safe_admin". If the logs indicate that user administrator is already created, it means the instance already started once and the password has already been set. Check the recovery options.
IRIS should now be available on the host interface, port 443, using HTTPS protocol by default. You can access it by navigating to https://hostip in your web browser.
Additional configuration 🛠️
Please see configuration for more details.
Kubernetes
Enterprises wishing to run their IRIS instance on their preferred managed Kubernetes platform can utilize the official Helm charts and/or Kustomize manifests for enhanced deployment and management, ensuring high availability and seamless scaling as demand fluctuates.
The deploy directory in the iris-web GitHub repository provides a starting point for deploying IRIS using EKS or GKE. Customize each variant with your values for a smooth deployment experience.
For more details, please visit the deploy directory on GitHub.
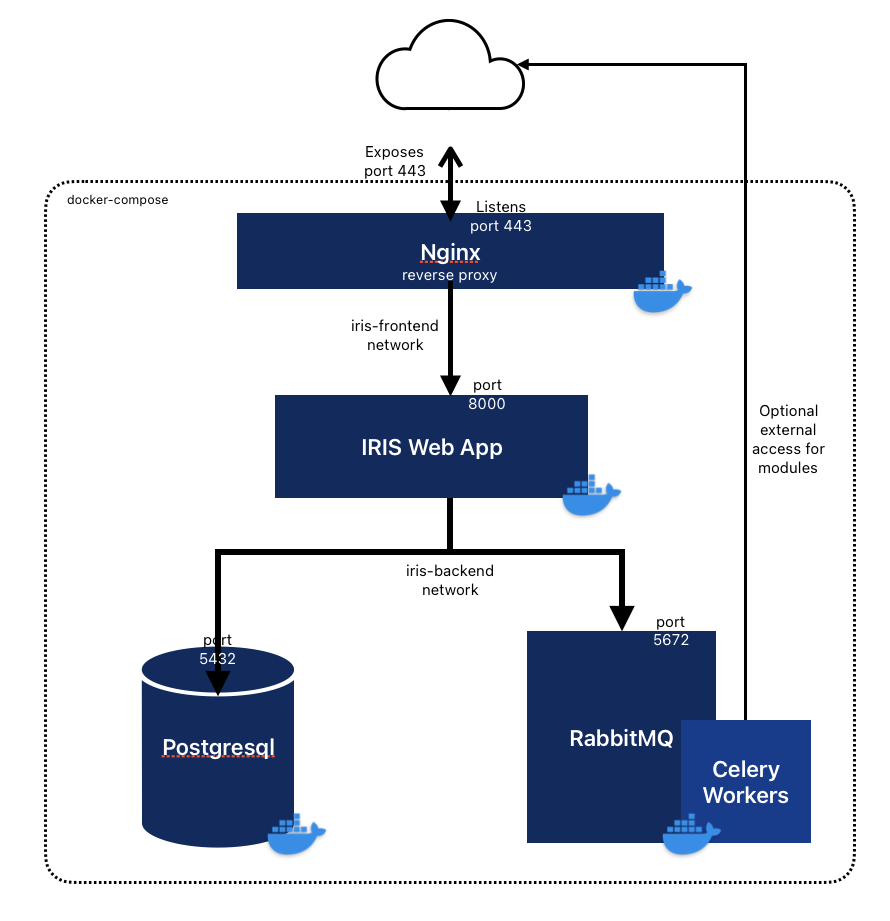
Components 📦
Note that IRIS is split into five Docker services, each with a different role:
app- iris_webapp: The core, including web server, database management, module management, etc.db: A PostgreSQL databaseRabbitMQ: A RabbitMQ engine to handle job queuing and processingworker: A job handler relying on RabbitMQnginx: A NGINX reverse proxy
Each service can be built independently, which is useful when developing. In this QuickStart, all services are built at once.